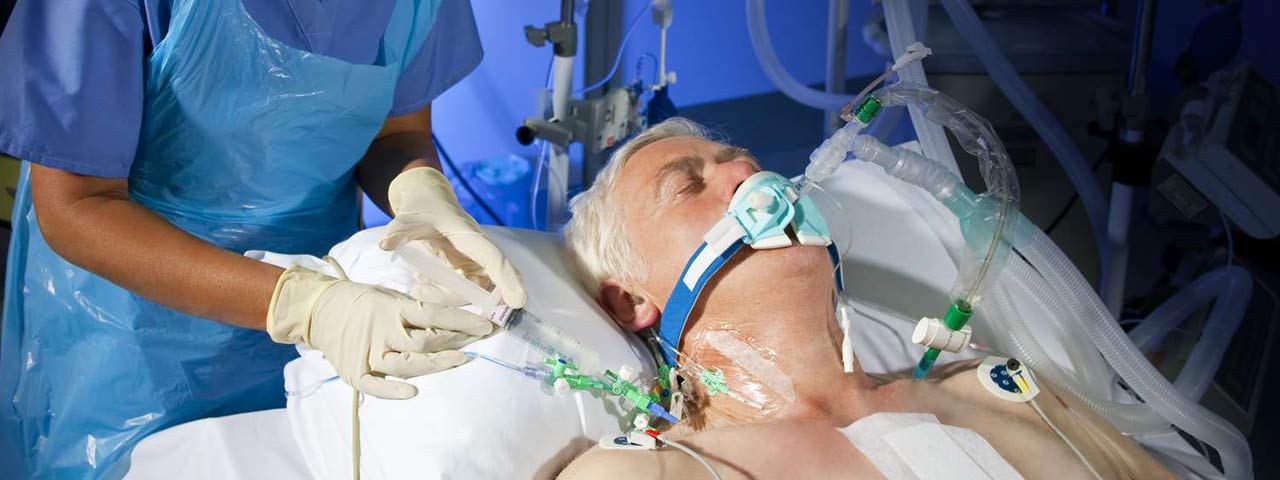
Medical Equipment refers to devices and instruments used in the diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, or rehabilitation of patients. These can be categorized based on their purpose, usage setting (home, hospital, clinic), and technological sophistication.
Let me know if you need assistance managing, categorizing, or documenting medical equipment data!
Types of Medical Equipment
1. Diagnostic Equipment
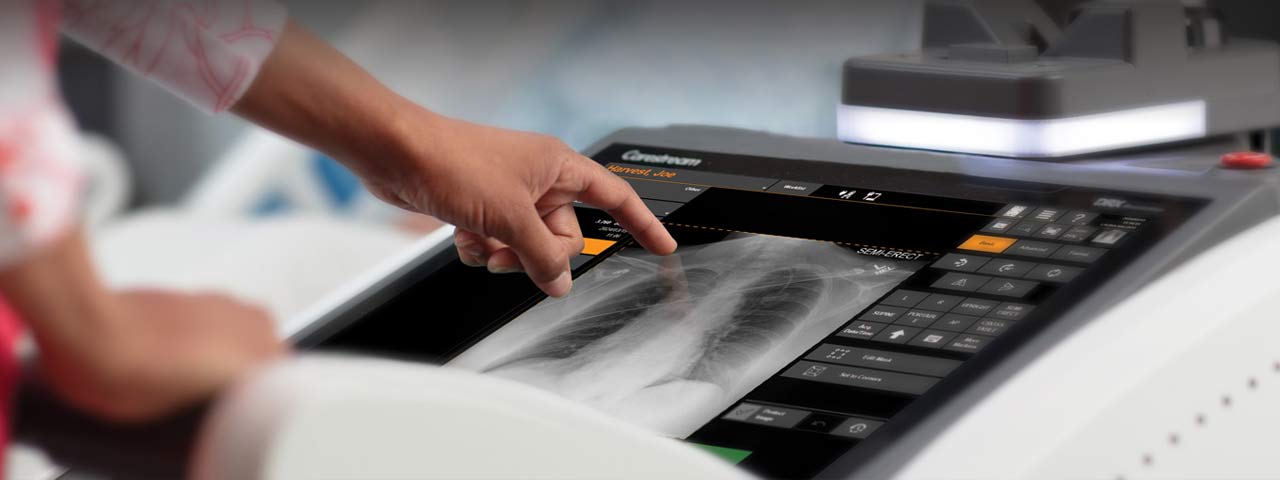
Used to identify and diagnose medical conditions. Examples:- X-ray machines
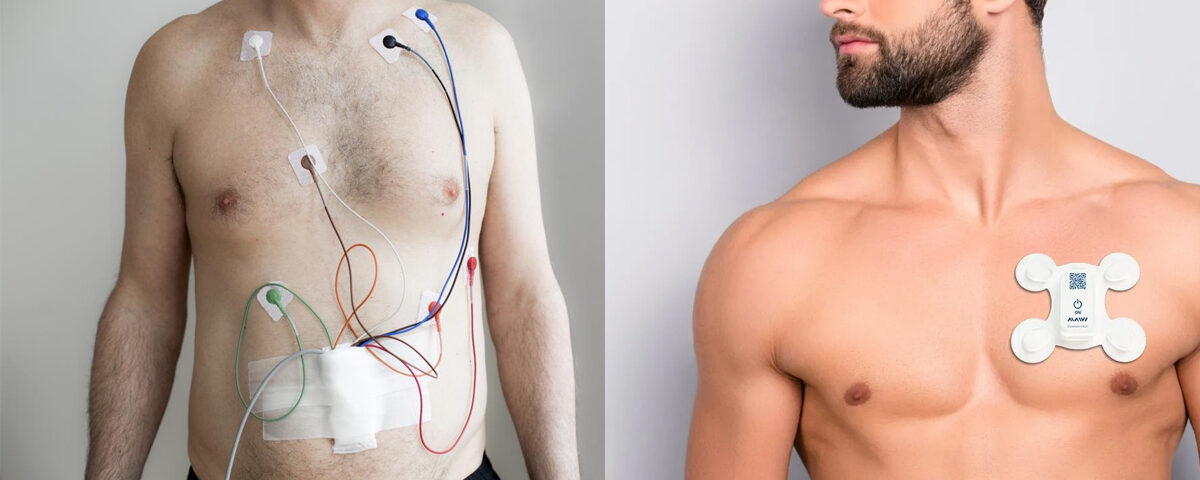
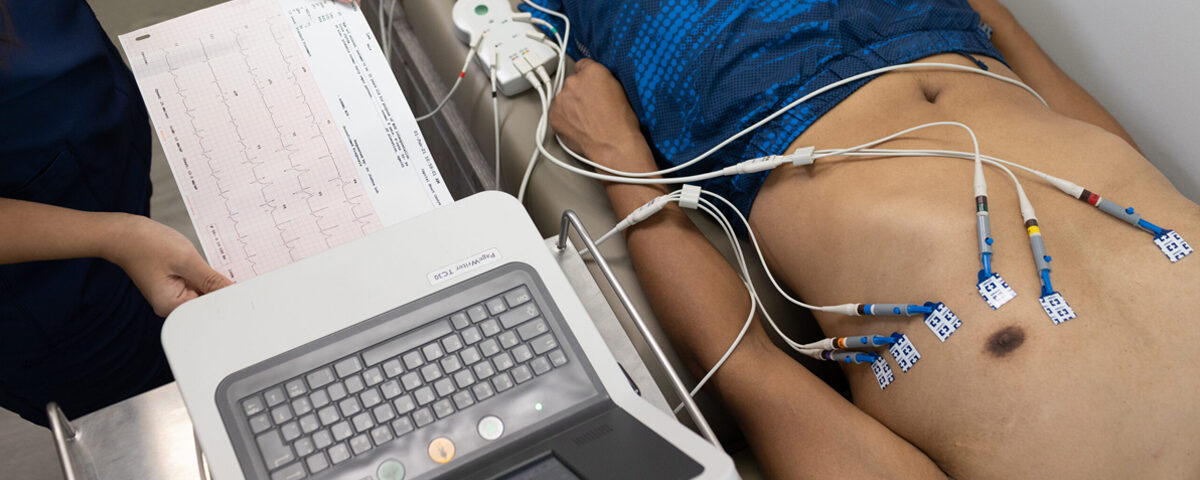
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) machines
- HOLTER monitoring
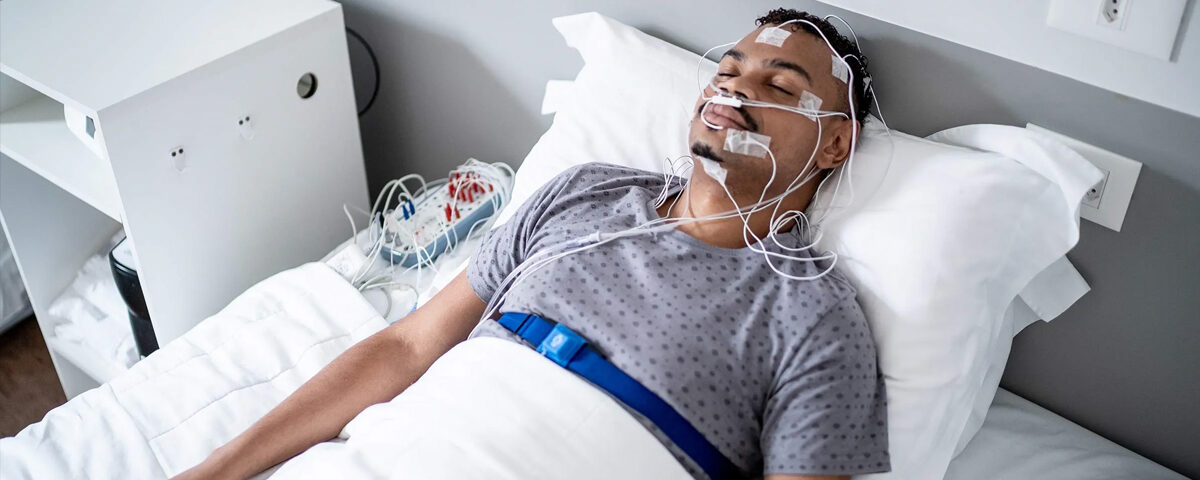
- SLEEP STUDY
2. Therapeutic Equipment
Used for treatment or physical rehabilitation. Examples:- Infusion pumps
- Dialysis machines
- Ventilators
- TENS units(pain relief)
- CPAP/BiPAP machines(sleep apnea therapy)
- OXYGEN CONCENTRATOR
- NEBULIZER MACHINE
- Portable suction machine
3. Monitoring Equipment
Used to track a patient’s vital signs or condition. Examples:- Pulse oximeters
- Blood pressure monitors
- Cardiac monitors/ Multipara monitors
- Blood glucose meters
- CONTINUOUS GLUCOSE MONITORING (CGM)
4. Life-Support Equipment
Used to sustain life during medical emergencies or critical care. Examples:- Ventilators
- Bipap & CPAP machine
- Syringe pump
- Oxygen cylinder
6. Home Medical Equipment (HME)
Used for ongoing treatment or rehabilitation at home. Examples:- Mobility aids(wheelchairs, walkers, crutches)
- Nebulizers(for respiratory therapy)
- Portable oxygen concentrators
- Hospital beds
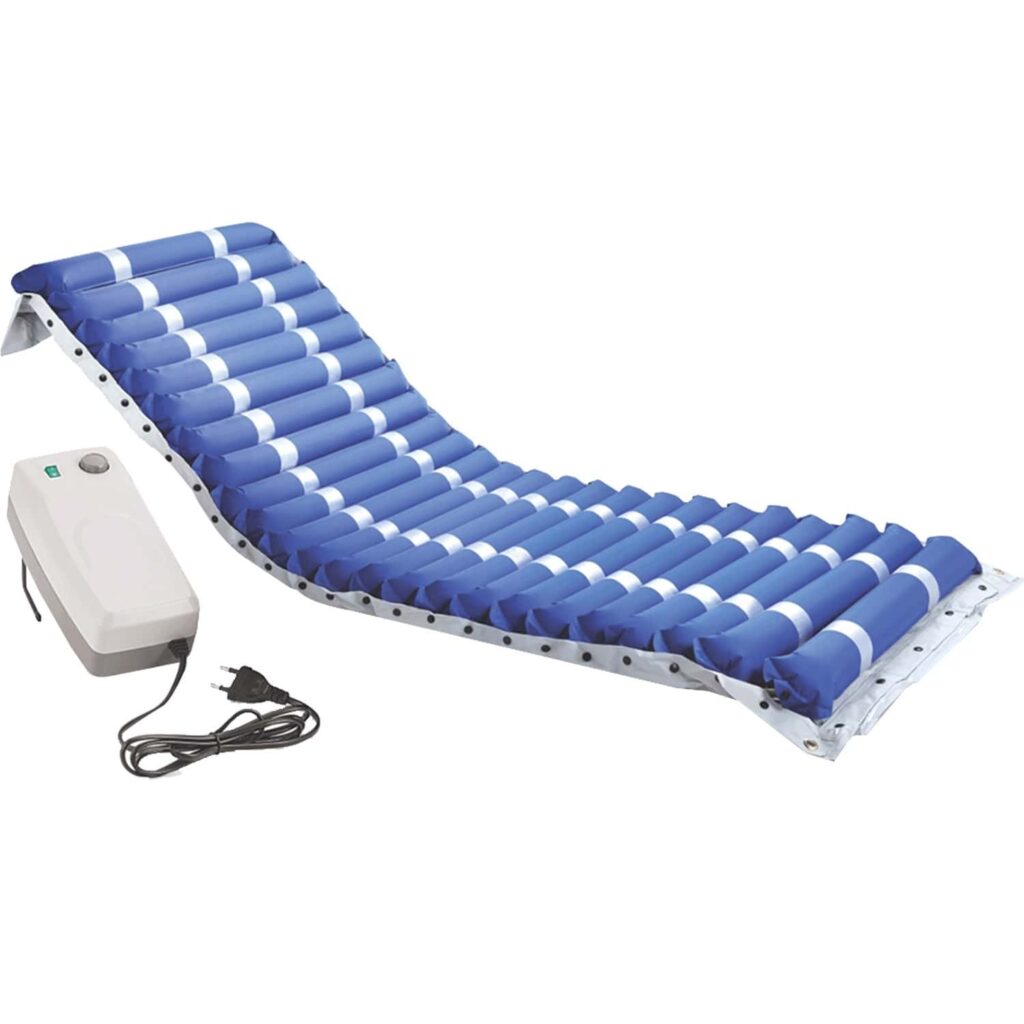
- Nimbus mattress
- Air mattress(for bedsore management)
- Suction machine
- Commodes or bedside toilets
7. Rehabilitation Equipment
Used for physical therapy and recovery. Examples:- Exercise bands and resistance devices
- Parallel bars(for gait training)
- Therapy balls
8. Laboratory Equipment
Used for analyzing samples in clinical labs. Examples:- Blood analyzers
- Microscopes
- Centrifuges
- PCR machines
- ELECTROLYTE ANALYZER
Features to Consider When Choosing Medical Equipment
- Purpose: Fit for diagnosis, treatment, monitoring, or support.
- Portability: Particularly important for home use.
- Ease of Use: User-friendly interfaces for patients and caregivers.
- Safety Standards: Compliance with regulatory guidelines (e.g., FDA, CE marking).
- Durability and Maintenance: Long lifespan and ease of servicing.
- Cost: Consider purchase, rental, and operational expenses.
- Training Requirements: Some devices need trained operators (e.g., ventilators).
Maintaining Medical Equipment
- Regular Calibration: Ensure devices provide accurate readings.
- Cleaning and Sterilization: Prevent cross-contamination.
- Inspection: Check for wear and tear or faulty components.
- Software Updates: For devices with integrated software (e.g., smart monitors).
- Storage Guidelines: Store as per the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain functionality.
Organizing Medical Equipment Data
If you are managing a list of medical equipment, you can structure it like this:| Equipment Name | Type | Purpose | Location | Last Serviced | Status |
| Portable X-Ray Machine | Diagnostic | Imaging | Radiology Dept. | 2024-01-05 | Functional |
| CPAP Machine | Home Equipment | Sleep Apnea Therapy | Patient’s Home | 2023-12-10 | Functional |
| Infusion Pump | Therapeutic | Fluid/Medication Delivery | General Ward | 2024-01-20 | Requires Service |
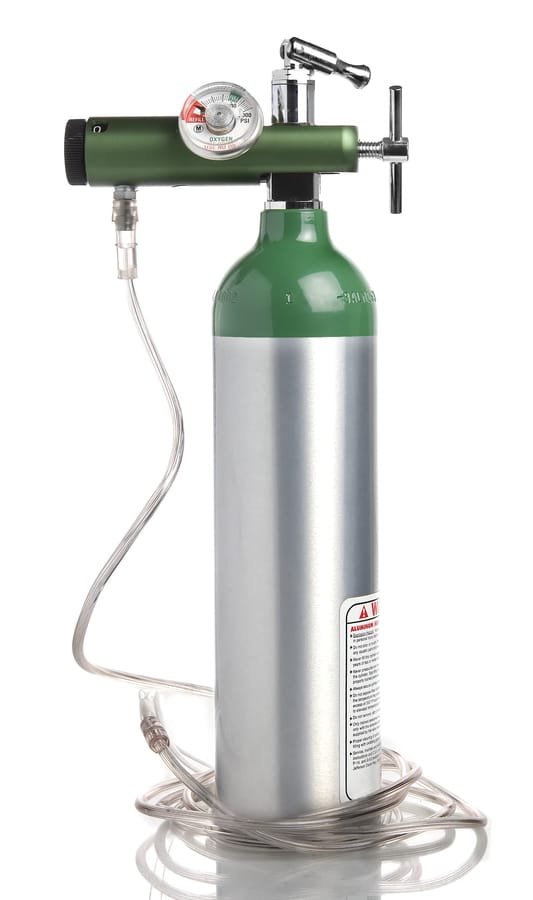

Oxygen cylinder
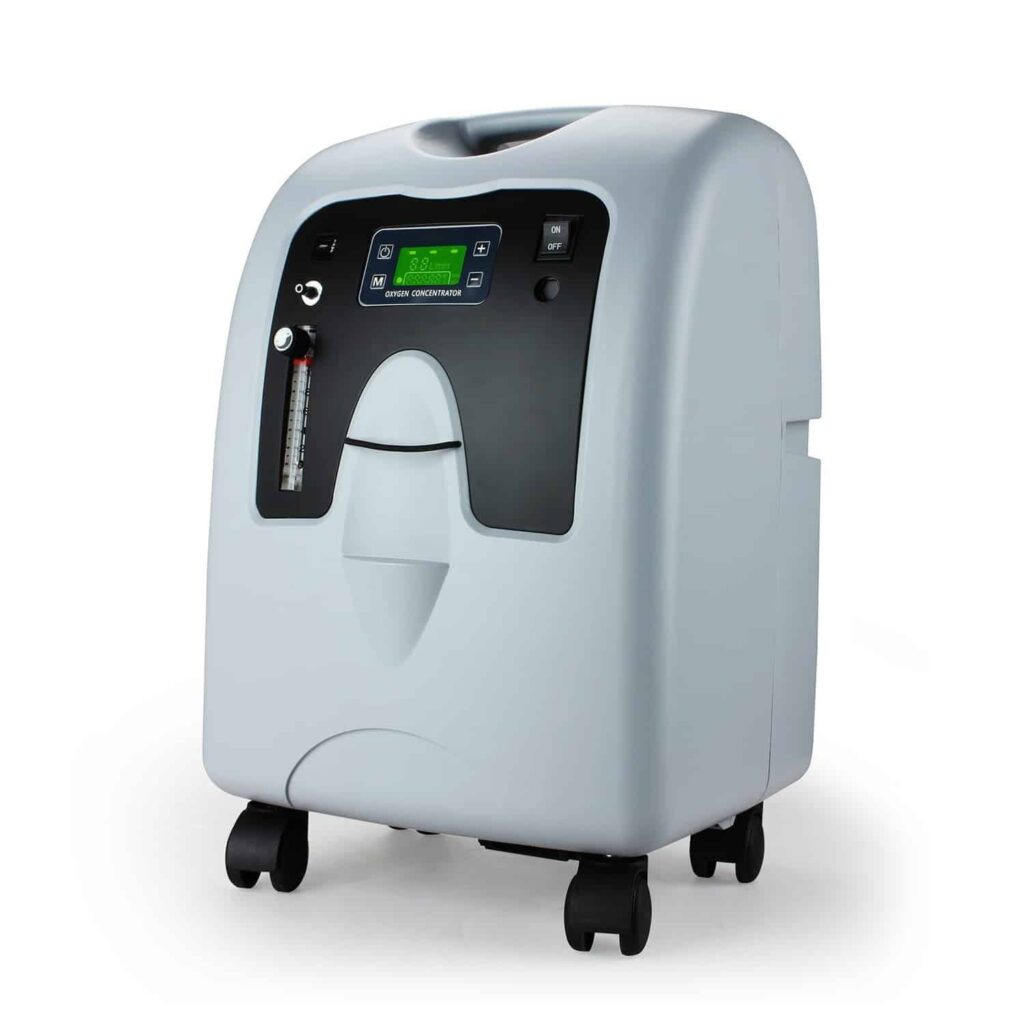

Oxygen concentrator
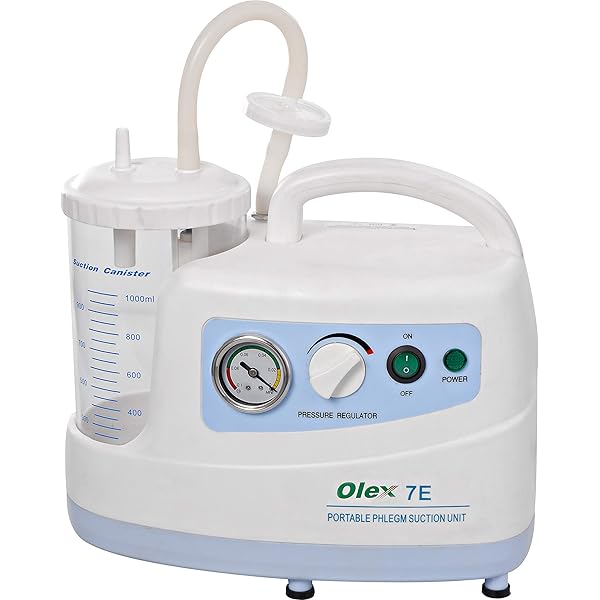
Suction machine (portable)
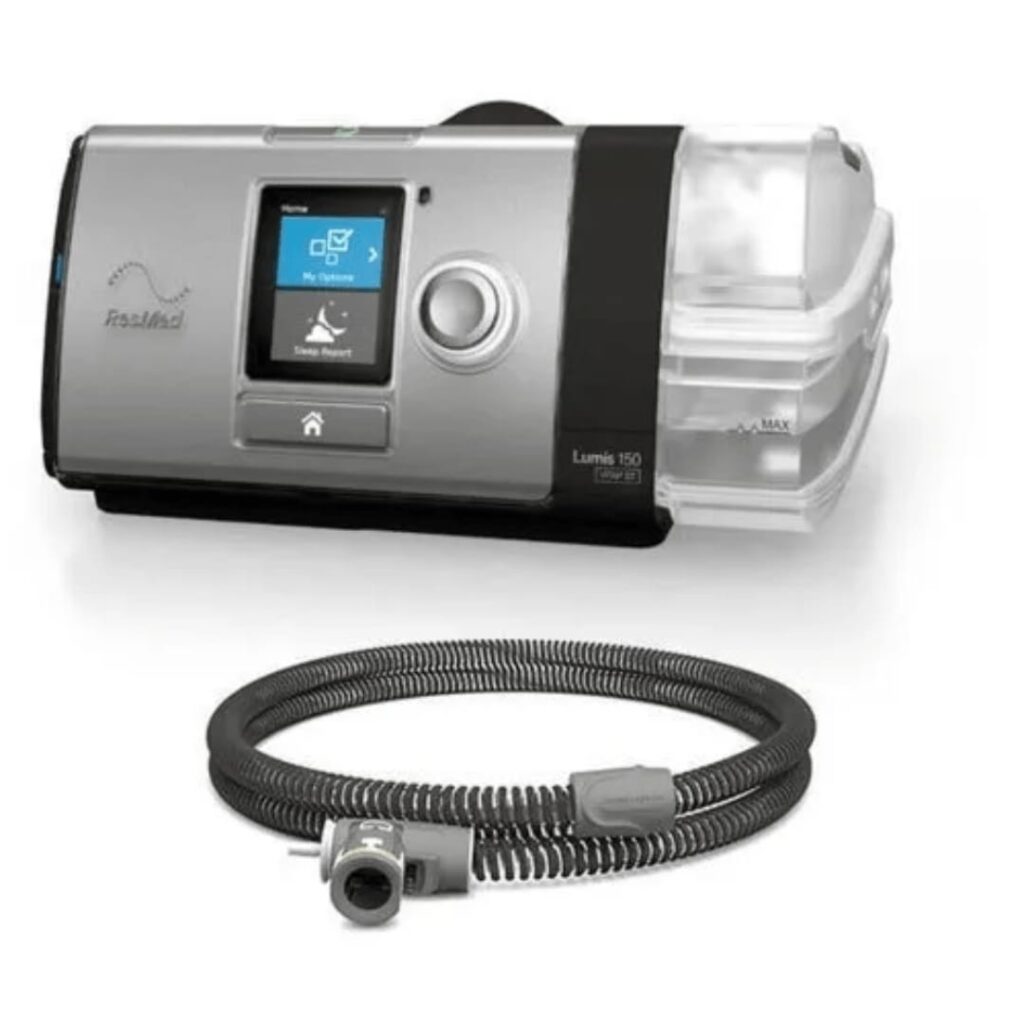

Bipap
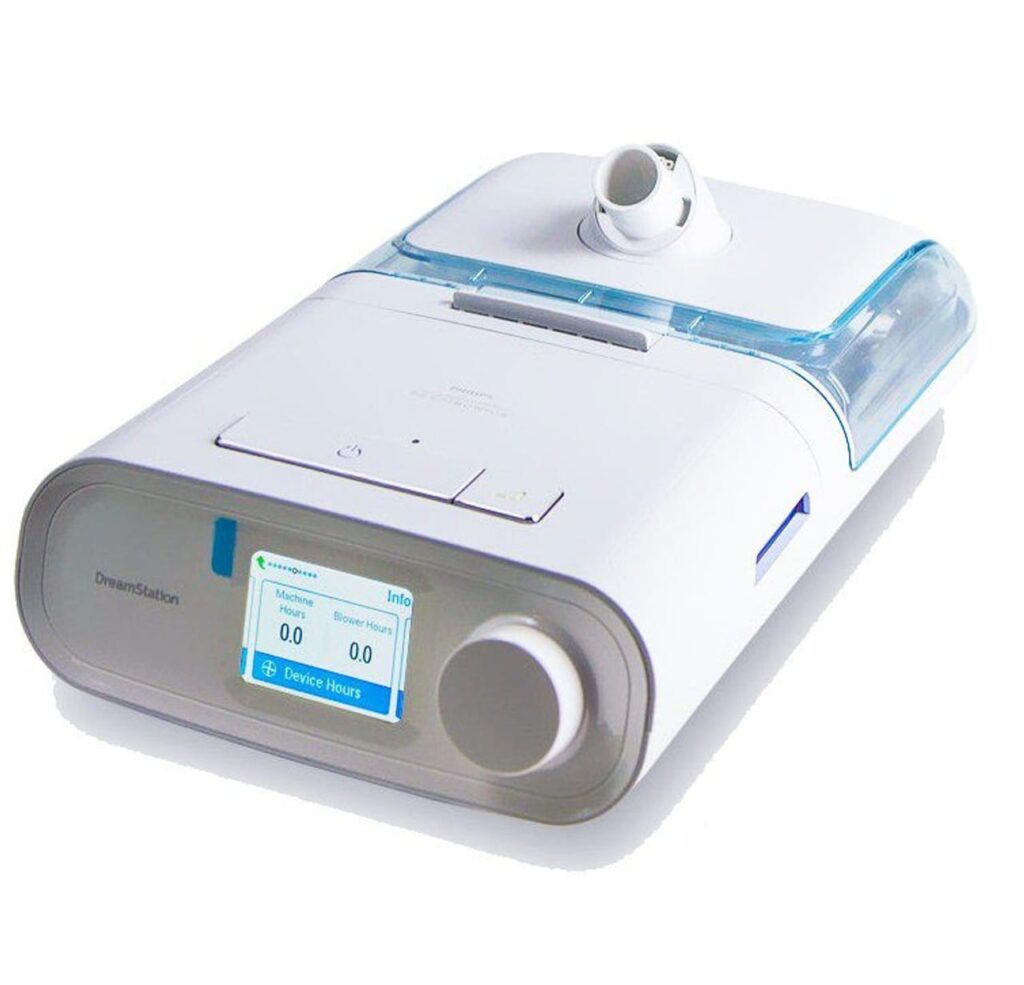
CPAP
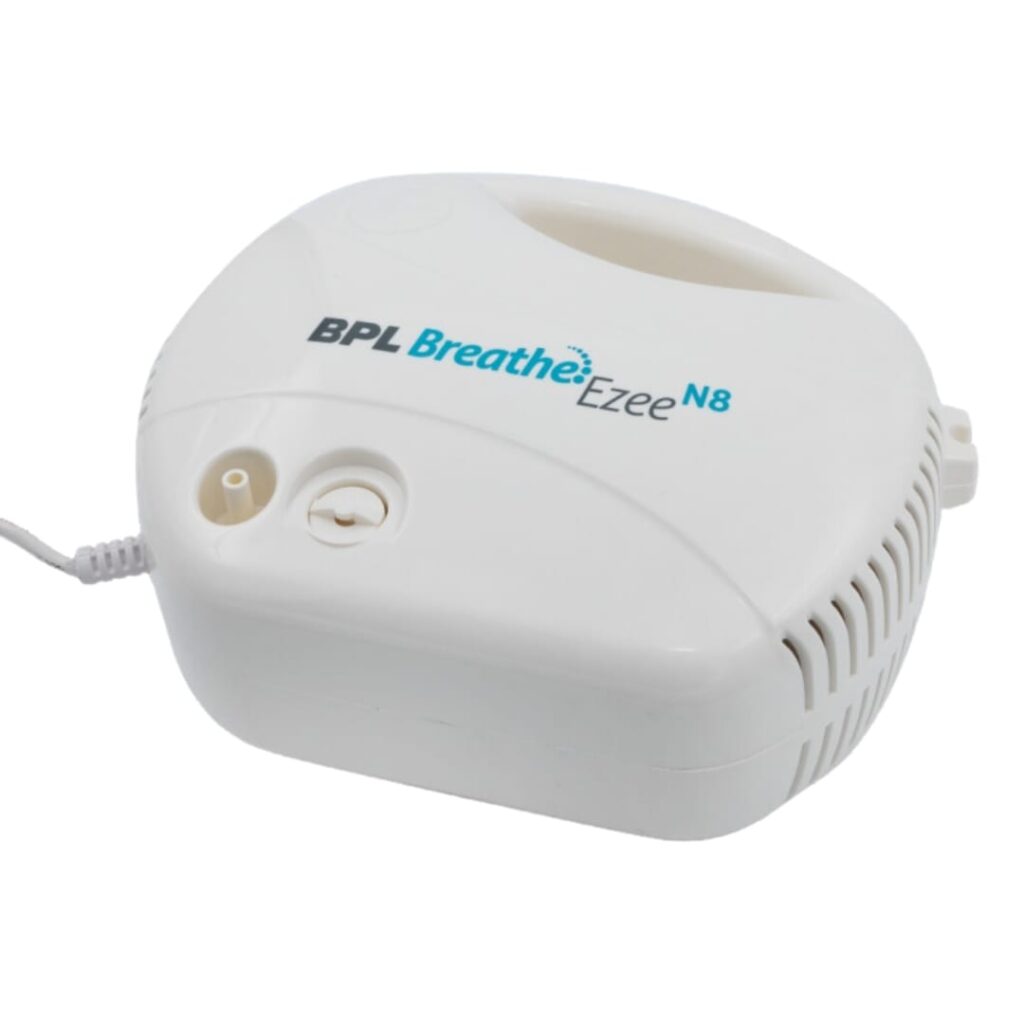

Nebulizer
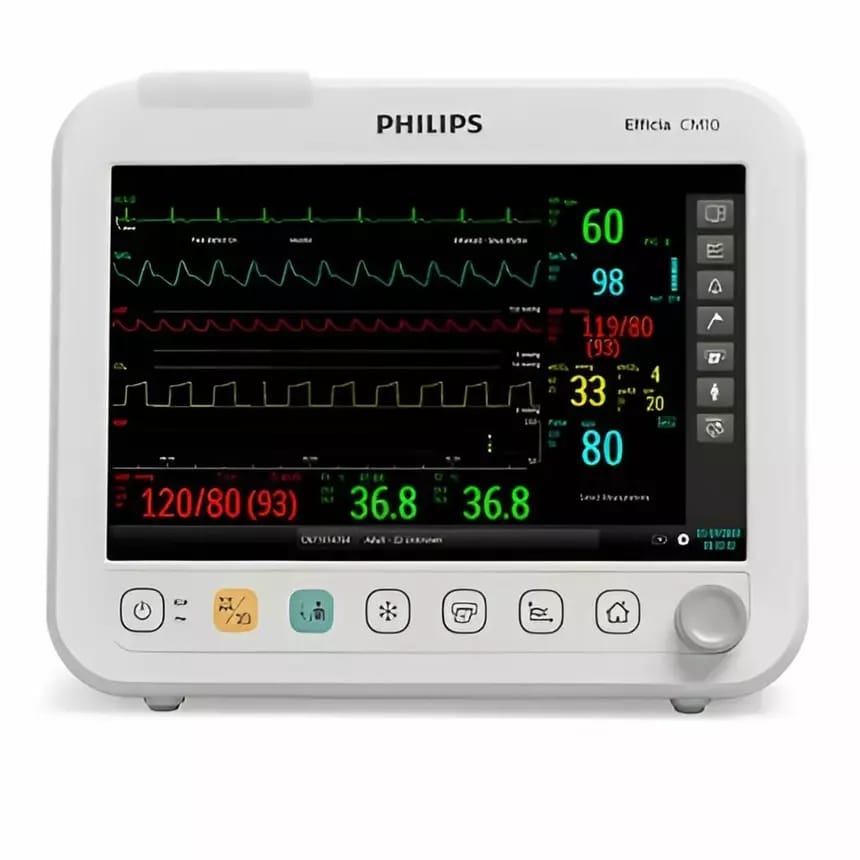
Cardiac monitor
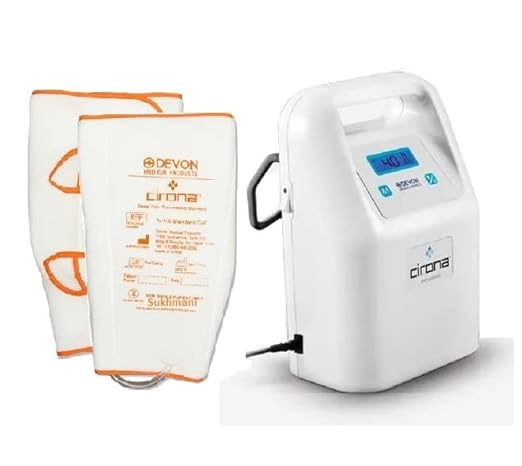
Dvt pump

Ventilator
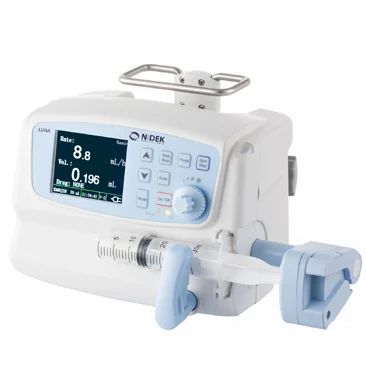
Syringe pump

Infusion pump
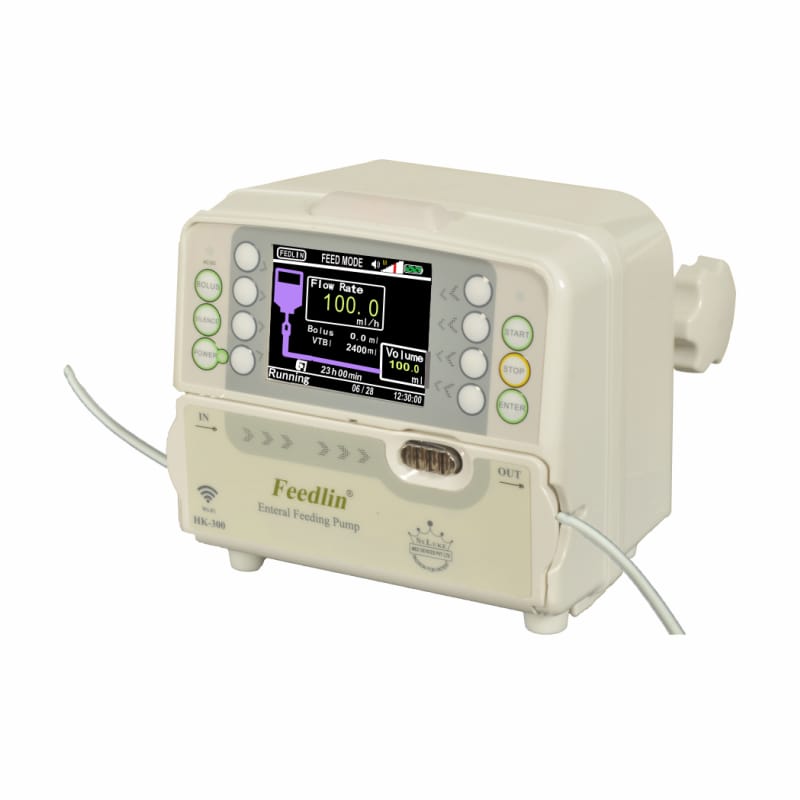
Feeding pump
Hfno
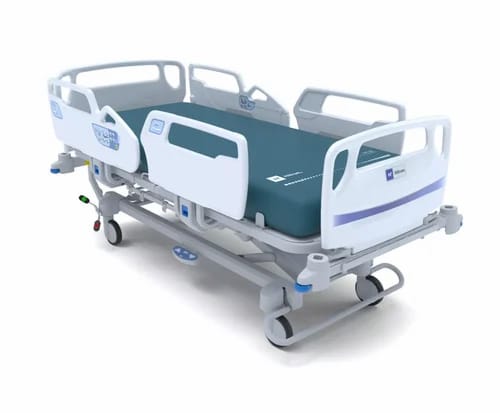

Hospital bed

IV stand
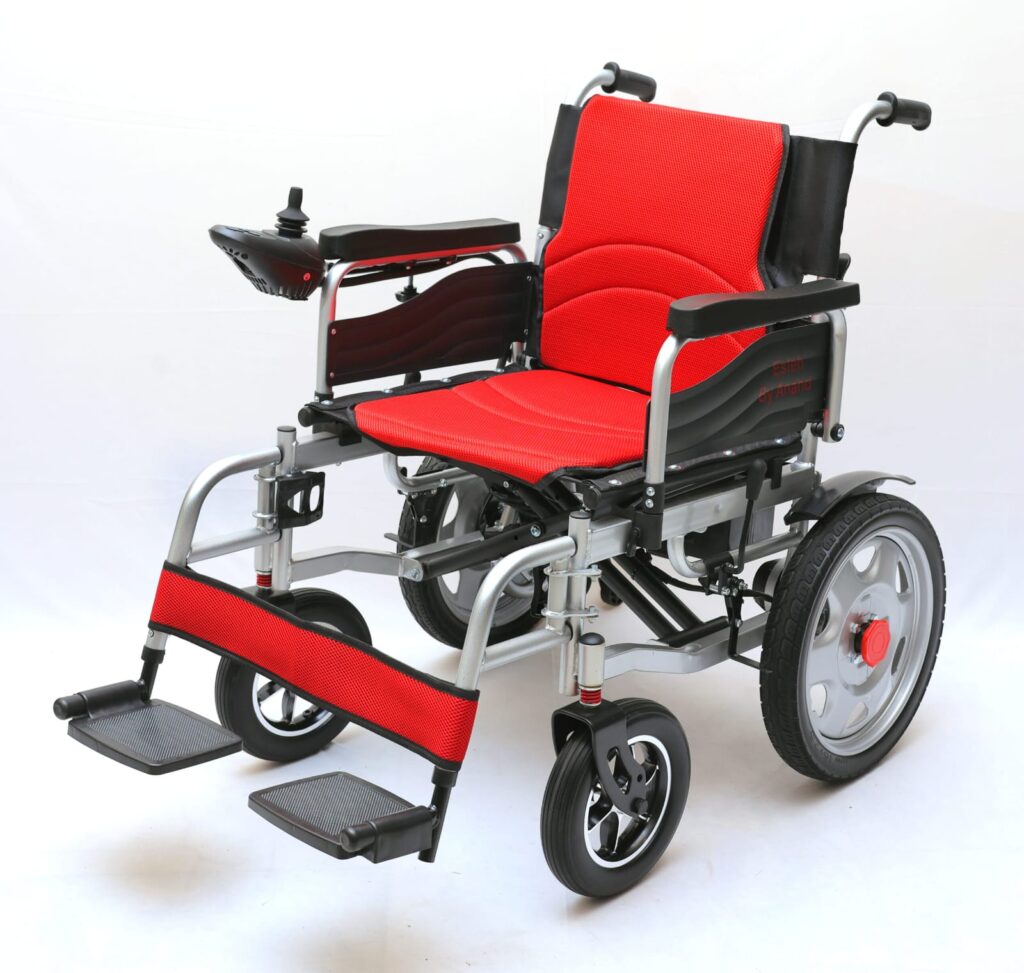

Wheel chair

Food table

Recliner Bed