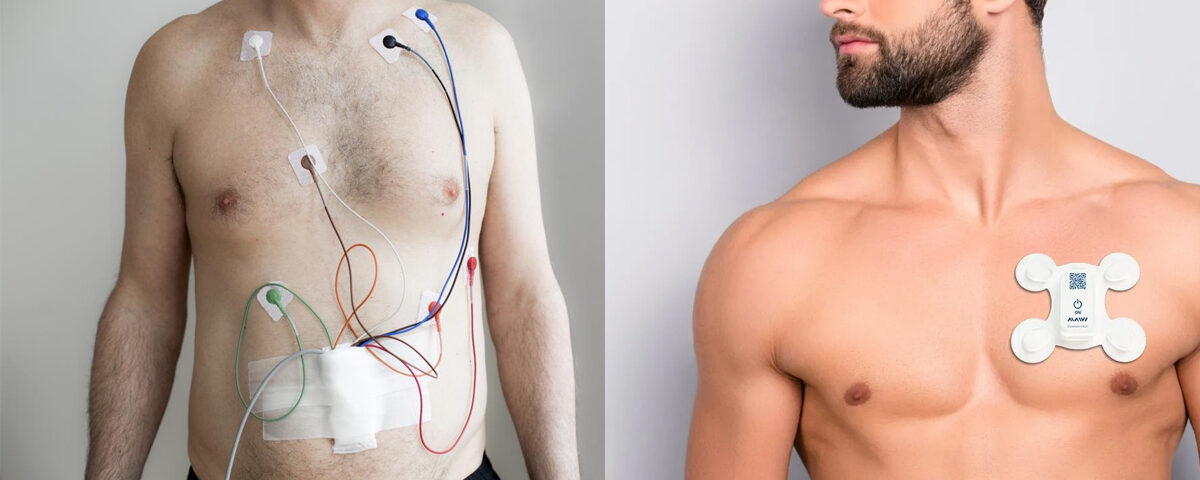
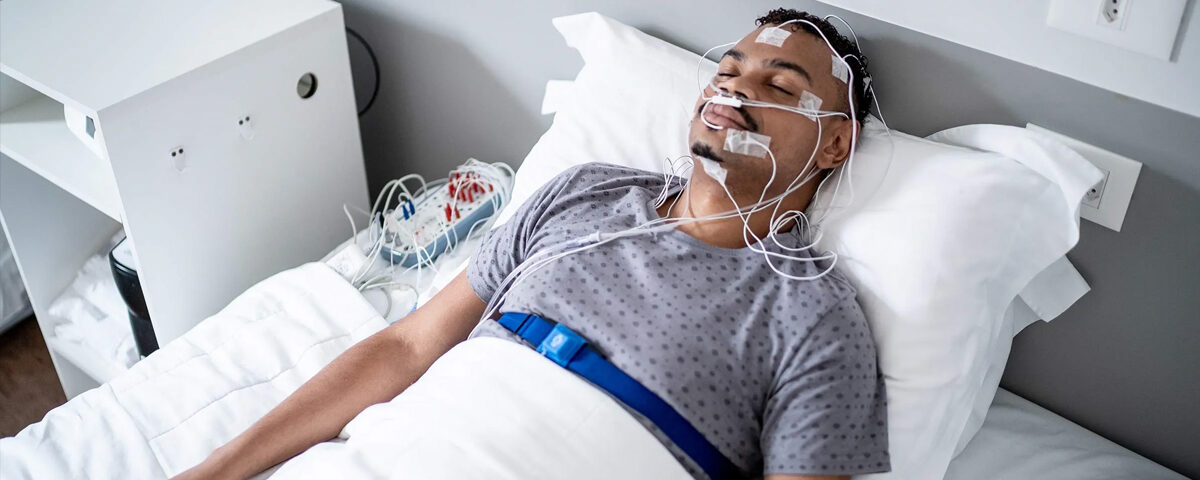
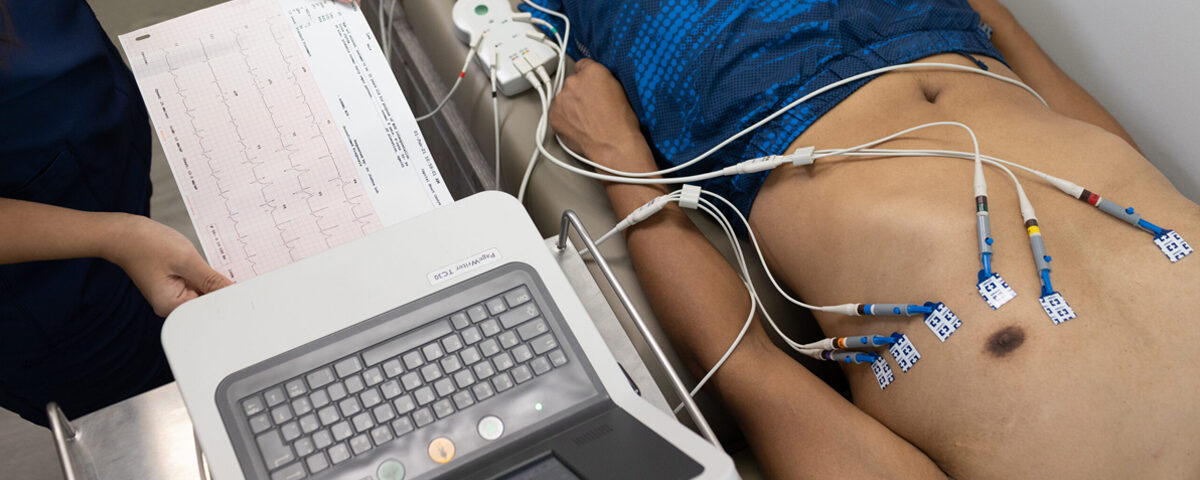
ECG stands for Electrocardiogram, which is a diagnostic tool used to measure and record the electrical activity of the heart over a period of time. It is commonly used to detect heart problems such as arrhythmias, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and other cardiac conditions.
Key Components of an ECG:
- P Wave: Represents atrial depolarization.
- QRS Complex: Represents ventricular depolarization.
- T Wave: Represents ventricular repolarization.
- PR Interval: Time between the start of atrial depolarization and the start of ventricular depolarization.
- ST Segment: Interval between ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- Heart Rate: Can be calculated from the rhythm strip.
Data You May Need:
If you’re asking about extracting data or analyzing ECG reports:
- Patient information (e.g., name, age, gender).
- Heart rate (in beats per minute).
- Rhythm type (e.g., normal sinus rhythm, arrythmia).
- Observed abnormalities (e.g., ST elevation, QRS widening).
- Interpretation/Conclusion.