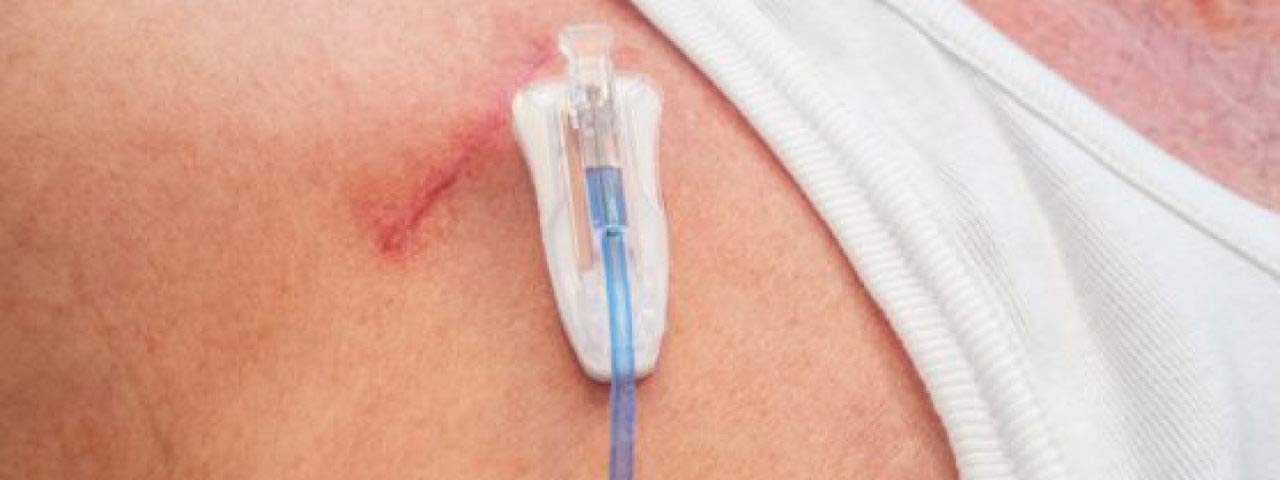
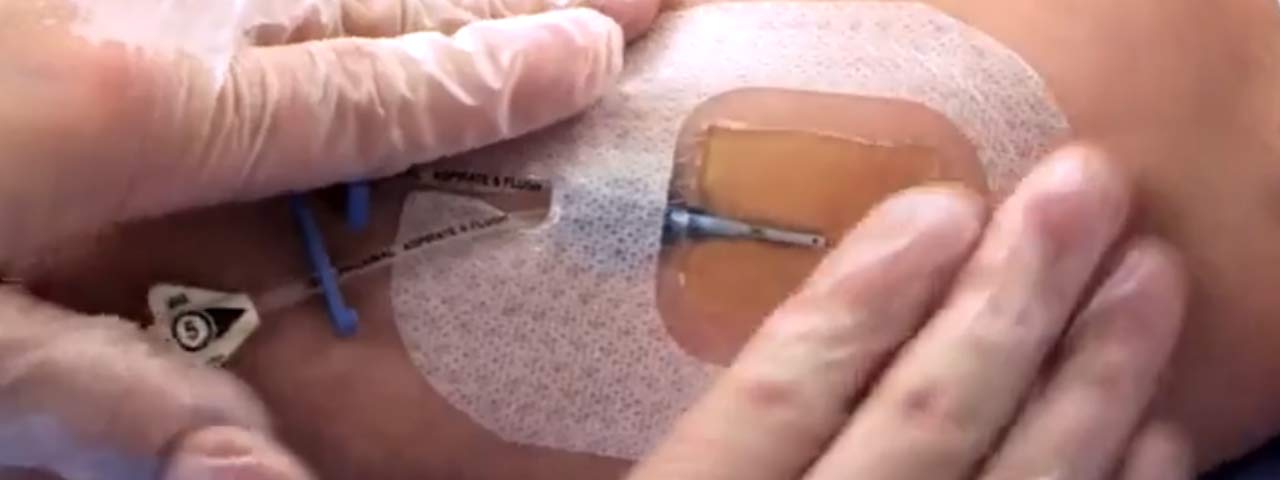
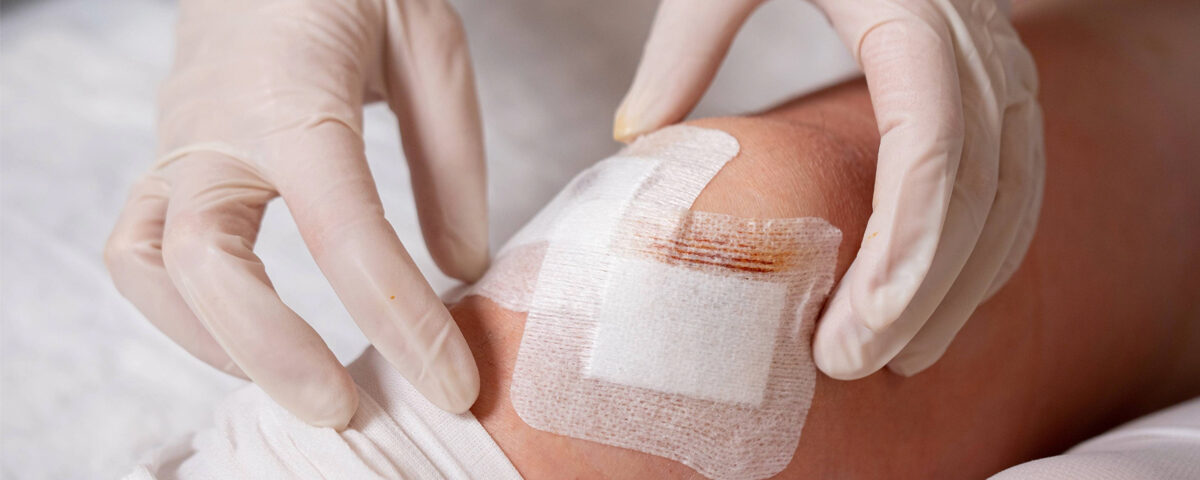
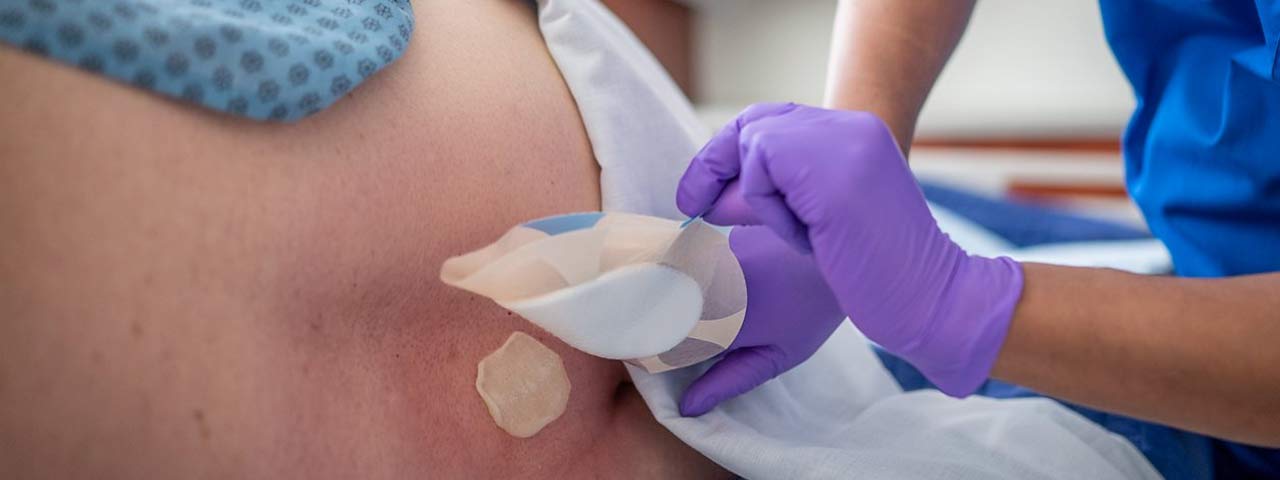
Dialysis line dressing is a critical procedure to maintain sterility and prevent infections in patients with central venous catheters (CVCs) used for hemodialysis. Proper dressing ensures the catheter remains secure and functional, protecting the insertion site from contamination.
Objectives:
- Maintain a sterile barrier around the catheter site.
- Prevent catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSIs).
- Ensure the line is secure to avoid dislodgment.
- Allow proper inspection of the insertion site.
Frequency of Dressing Change:
- Transparent dressings: Change every 7 days or if compromised (wet, soiled, or loose).
- Gauze dressings: Change every 48 hours.
- Immediately after dialysis sessions, if contamination occurs.
Equipment Required:
- Sterile dressing kit.
- Antiseptic solution (chlorhexidine gluconate 2% with alcohol or povidone-iodine).
- Sterile gloves and gown.
- Face mask for both caregiver and patient.
- Transparent dressing or sterile gauze and tape.
- Catheter securement device (if required).
- Biohazard waste bag for disposal.
Procedure Steps:
-
Preparation:
-
Explain the Procedure:
- Inform the patient about the purpose and steps involved.
-
Ensure Asepsis:
- Wash hands thoroughly.
- Wear a mask, sterile gloves, and a gown.
-
Position the Patient:
- Have the patient lie comfortably with the catheter site easily accessible.
-
Removing the Old Dressing:
- Don clean gloves.
- Carefully remove the old dressing, avoiding excessive movement of the catheter.
- Inspect the catheter site for:
- Redness, swelling, or discharge (indicating infection).
- Any signs of bleeding or irritation.
- Discard the old dressing in a biohazard bag.
- Cleaning the Insertion Site:
- Remove gloves and perform hand hygiene.
- Put on sterile gloves.
- Use antiseptic solution to clean:
- Start at the insertion site and work outward in a circular motion.
- Allow the area to dry completely (crucial for chlorhexidine).
-
Applying the New Dressing:
- Place a sterile transparent dressing or gauze over the cleaned site.
- Secure the dressing with tape if using gauze.
- Ensure no part of the catheter is exposed outside the sterile field.
- Securing the Catheter:
- Use a catheter securement device if needed to prevent movement.
- Ensure all connections are tight and covered with caps.
Post-Procedure Care:
- Check Dressing Integrity:
- Ensure it is intact, secure, and free of wrinkles or gaps.
- Patient Education:
- Advise the patient to avoid touching the dressing or getting it wet.
- Documentation:
- Record the date and time of the dressing change.
- Note any abnormalities (e.g., signs of infection).
Signs to Monitor for Infection:
- Local signs: Redness, swelling, warmth, or pus at the insertion site.
- Systemic signs: Fever, chills, or malaise.
Preventing Catheter-Related Infections:
- Maintain strict aseptic technique during dressing changes.
- Use chlorhexidine for skin antisepsis.
- Avoid frequent handling of the catheter.
- Replace dressings immediately if soiled or loose.
Would you like additional details on specific dressing types or troubleshooting complications like catheter dislodgment or suspected infection?